28 February 2018 | Updated on 1 March 2018
Do you know how to create a successful work breakdown structure?
As we all know, no matter how big the task you can get on top of it by organising it into manageable chunks. If you are struggling to work out how to organise the tasks within your project, an effecti...
As we all know, no matter how big the task you can get on top of it by organising it into manageable chunks. If you are struggling to work out how to organise the tasks within your project, an effective work breakdown structure (WBS, found in the APM Body of Knowledge and the PMBOK Guide, Sixth Edition) helps you to work out how to arrange each piece of work, and helps you regain control.
It breaks down key project deliverables into smaller, more digestible chunks as part of a hierarchical framework, so you can see what needs to be achieved each step of the way.
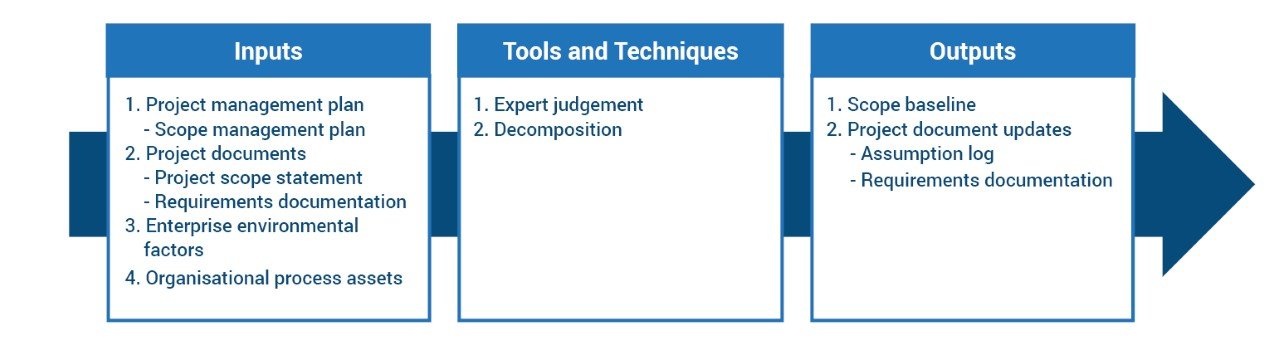
As you can see, a WBS comprises of inputs, tools and techniques, and outputs:
Inputs
This could include any of the following:
- A project scope statement or description identifying the main deliverables
- A list of requirements from you stakeholders
- Any process assets within your organisation
- Do you have existing templates for a work breakdown?
- Are there lessons learned that you can incorporate into the WBS?
Tools and techniques
Decomposition is the main technique that we use to create a WBS. This technique involves sub-dividing the work into increasingly smaller or more manageable chunks until it can be captured in a work package – i.e. it can be given to a specific resource to execute.
When structuring a WBS, there are a number of approaches to decomposition that will help to clarify the outputs. For example, using phases of the project as the first level of decomposition, with products as the second layer; or using major deliverables as the first level, and components of those deliverables as the second level.
Outputs
The primary output of this activity is a graphic showing the parent/child relationships between the levels. The immediate benefit is to clarify the scope and show how the work could be divided up as a way of engaging your team in further planning.
Some projects will benefit from a WBS dictionary, which provides reference information about the deliverables that is not illustrated in the graphic (required resources, cost estimates, acceptance criteria, etc. In PRINCE2® this information would be captured in product descriptions).
When the WBS is completed it can be added to a scope baseline or project plan.
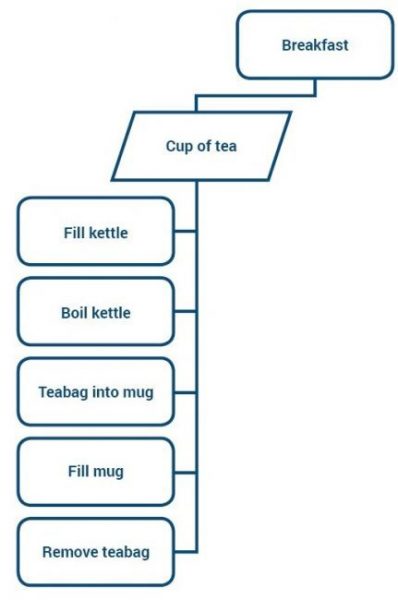
But what does this look like in practice, or in everyday terms, for those of us new to project management? Take making a cup of tea as part of your breakfast – it’s a simple enough task, right? Seen through a WBS lens, it would run as follows:
So, what’s the best way to begin?
We recommend that with your first venture you just go for it – dive in head first, but you’ll likely find that your first draft goes into a minute level of detail that’s actually unnecessary. But once that’s out of your system, you can create your next WBS collaboratively with your peers and get advice from other experienced project managers.
By all means, start by getting your ideas down on paper, but then get another project manager to review it. Ask them questions, such as: how should you cluster tasks together, and what levels of task they have used – do they focus on activities or outputs?; and does the risk of taking a long time to plan something outweigh the risk of just doing it and potentially getting it wrong?
Of course, the best way to learn is by doing. Our APM and PMP® courses go into greater detail about creating a successful WBS, and cover everything you need to know to gain the qualifications, so why not book onto a course right now?